What is the Process of Non-Contact Hot Plate Welding?
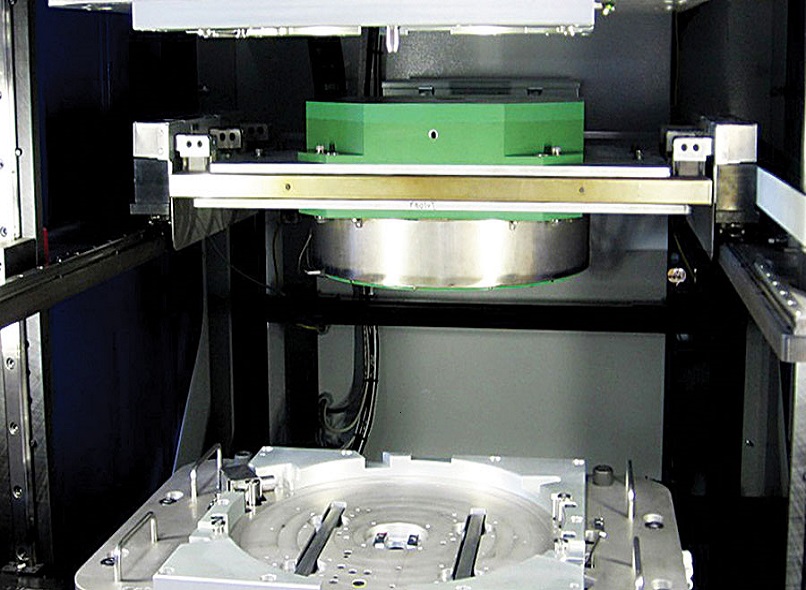
Non-contact hot plate welding is a highly advanced and innovative technique used in joining thermoplastic materials without the need for direct physical contact. This cutting-edge welding process offers numerous advantages over traditional welding methods, including reduced part distortion, improved weld strength, increased design flexibility, enhanced production efficiency, greater versatility in material compatibility, environmental sustainability, potential cost savings, and exciting recent technological advancements.
The process of non-contact hot plate welding begins with thorough preparation of the two thermoplastic parts that are to be joined. The surfaces of the parts are meticulously cleaned and positioned in the welding fixture, ensuring precise alignment. A non-contact hot plate, typically made of a conductive material such as aluminum, is then heated to a specific and controlled temperature.
Unlike traditional hot plate welding, which involves direct contact between the parts and the heated plate, non-contact hot plate welding takes a different approach. Instead of physically touching the hot plate, the thermoplastic parts are brought close to the heated plate without direct contact. Through the process of conduction, the heat from the plate is transferred to the surfaces of the parts, softening the material and allowing for bonding. This non-contact approach minimizes the risk of damage to the parts, especially for sensitive or delicate materials, while still achieving excellent weld quality.
As the parts are heated, pressure is applied to ensure proper contact between the softened surfaces. The pressure promotes intimate contact and facilitates the formation of a strong and durable bond. The duration of the heating and pressure application is carefully controlled to achieve optimal weld strength while avoiding overexposure to heat. This precise control ensures the integrity of the welded joint and prevents any compromise in the mechanical properties of the final product.
One of the notable advantages of non-contact hot plate welding is its ability to significantly reduce part distortion. Since the parts do not come into direct contact with the hot plate, there is less risk of warping or deformation. This is particularly beneficial for precision components or parts with intricate geometries, where maintaining dimensional accuracy is critical. The non-contact approach allows for greater control over the heating process, resulting in minimal thermal stress and distortion.
Furthermore, non-contact hot plate welding offers improved weld strength compared to traditional welding methods. The controlled heating process allows for better material penetration and molecular interdiffusion, resulting in a stronger bond between the thermoplastic parts. The absence of physical contact during the heating phase also reduces the risk of contaminants being trapped in the weld, further enhancing the weld quality. This exceptional weld strength ensures the longevity and durability of the joined parts, making non-contact hot plate welding a preferred choice for applications that require high structural integrity.
In addition to its technical advantages, non-contact hot plate welding provides increased design flexibility. The non-contact nature of the process allows for the joining of thermoplastic parts with varying shapes, sizes, and geometries. This opens up possibilities for complex assemblies and multi-material structures, enabling manufacturers to create innovative and efficient designs. The ability to join dissimilar materials expands the range of applications for non-contact hot plate welding, making it a versatile choice for various industries.
Moreover, non-contact hot plate welding contributes to enhanced production efficiency. The precise temperature control and reduced cycle times result in faster welding processes, leading to increased productivity. This is particularly advantageous for high-volume production environments where time and cost savings are crucial. The non-contact approach also reduces the need for post-welding cleaning or finishing, streamlining the overall manufacturing process and reducing production costs.
Another significant advantage of non-contact hot plate welding is its environmental sustainability. The process eliminates the need for consumables such as adhesives or fasteners, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, the precise heating control of non-contact hot plate welding ensures energy efficiency, minimizing energy consumption and reducing carbon footprint. This aligns with the growing demand for sustainable manufacturing practices and contributes to a greener future.
Furthermore, non-contact hot plate welding has the potential for cost savings. While the initial investment in the equipment and setup may be higher compared to traditional welding methods, the long-term benefits can outweigh the costs. The reduced part distortion and improved weld strength minimize the need for rework or repairs, saving both time and money. Additionally, the increased design flexibility allows for more efficient use of materials, reducing waste and optimizing production processes.
Recent technological advancements have further enhanced the capabilities of non-contact hot plate welding. For instance, the integration of temperature sensors and feedback control systems enables more precise temperature regulation, resulting in improved weld quality and consistency. Material innovations have also played a crucial role, with the development of new thermoplastic materials that exhibit better melt flow, higher strength, enhanced chemical resistance, and improved heat resistance. These advancements have expanded the range of industries and products where hot plate welding can be applied.
Non-contact hot plate welding finds applications in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, consumer goods, and more. It is commonly used for joining thermoplastics such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polycarbonate, and other similar materials. This versatile welding technique is suitable for various components, from small intricate parts to large structural assemblies.
In conclusion, non-contact hot plate welding is a highly efficient, reliable, and technologically advanced method for joining thermoplastic materials. Its numerous advantages, including reduced part distortion, improved weld strength, increased design flexibility, enhanced production efficiency, greater material compatibility, environmental sustainability, potential cost savings, and recent technological advancements, make it an attractive choice for manufacturers in various industries. By utilizing the non-contact approach and leveraging the precise temperature control, manufacturers can achieve high-quality welds while optimizing their production processes, meeting the demanding requirements of modern applications, contributing to a more sustainable future, and potentially realizing cost savings in the long run.





