What is the Process of Hot Plate Welding PVC?
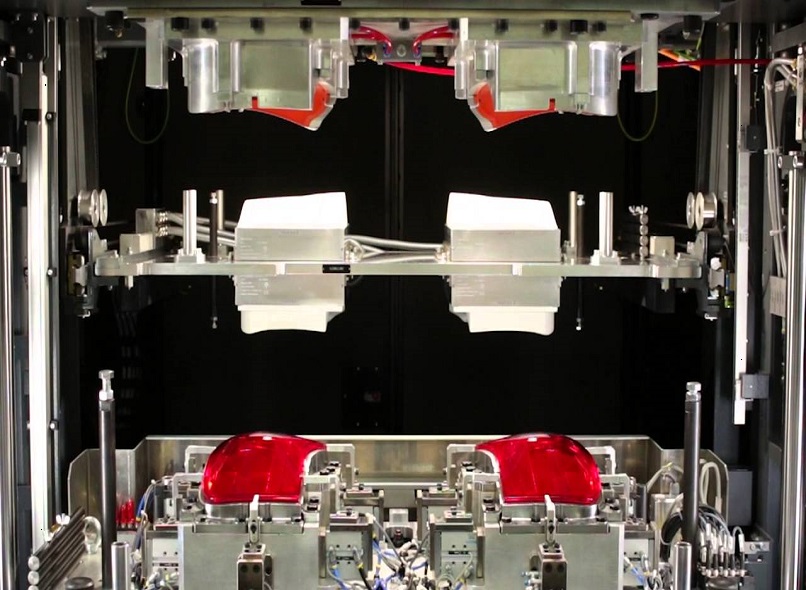
Hot plate welding is a commonly used technique for joining thermoplastic materials, including PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride). In this article, we will explore the process of hot plate welding PVC and how it is performed.
Introduction to Hot Plate Welding
Hot plate welding is a type of heat-based welding method that uses a heated platen to melt and join thermoplastic materials together. It is widely used in various industries for its ability to create strong and durable bonds. This versatile welding technique has found applications in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, packaging, and medical.
The Process of Hot Plate Welding PVC
The process of hot plate welding PVC involves several steps, each crucial for achieving a successful weld:
- Preparation: Before starting the hot plate welding process, it is crucial to prepare the PVC materials. This includes cleaning the surfaces to be welded and ensuring they are free from any contaminants or debris. Proper preparation is essential to achieve optimal adhesion and a strong bond. Additionally, it is important to consider the design and geometry of the PVC parts to ensure proper alignment during the welding process.
- Heating: The next step is to heat the hot plate to the desired temperature. The temperature required for PVC welding typically ranges from 200 to 250 degrees Celsius. It is important to maintain a consistent and controlled temperature throughout the welding process. Temperature regulation is critical to avoid overheating or damaging the PVC material. Advanced hot plate welding systems incorporate temperature sensors and feedback control systems to ensure precise temperature regulation.
- Clamping: Once the hot plate reaches the desired temperature, the PVC parts to be welded are placed between the platen and held firmly in place using clamps or a pneumatic press. This ensures proper alignment and contact between the surfaces to be welded, creating a tight joint. The clamping force applied should be sufficient to maintain contact between the molten surfaces and promote material flow and bonding.
- Heating and Melting: The heated platen is then brought into contact with the PVC surfaces to be welded. The heat from the platen melts the surfaces, creating a molten layer. The temperature and heating time are carefully controlled to ensure proper melting and avoid degradation of the PVC material. The heating time depends on factors such as the thickness and thermal conductivity of the PVC parts.
- Joining: After the surfaces have melted, the platen is removed, and the molten surfaces are quickly pressed together. This creates a strong bond as the molten material solidifies. Pressure is maintained on the joint until the molten material cools and solidifies completely. The amount of pressure applied and the duration of pressure application depend on the specific PVC material being welded. Advanced hot plate welding systems allow for precise control of pressure and enable real-time monitoring of the welding process.
- Cooling and Solidification: Once the joint has cooled and solidified, the clamps or press are released, and the welded PVC assembly can be further processed or used as required. Cooling is an essential step to ensure the long-term strength and stability of the weld. The cooling time required may vary depending on factors such as the material thickness and ambient temperature. Proper cooling ensures that the weld joint achieves its desired mechanical properties.
- Post-Weld Inspection and Finishing: After the cooling process, it is important to inspect the weld joint for any defects or imperfections. This can be done visually or using non-destructive testing methods to ensure the quality of the weld. Any excess material or flash can be carefully removed using appropriate tools to achieve the desired final shape and appearance. Post-weld finishing processes may be required, such as polishing or smoothing, to enhance the aesthetics of the welded PVC assembly.
Advantages of Hot Plate Welding PVC
Hot plate welding offers several advantages when it comes to joining PVC materials:
- Strong and Durable Joints: Hot plate welding creates robust and long-lasting joints that can withstand various stresses and environmental conditions. The resulting welds have mechanical properties comparable to the original PVC material, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the assembled products.
- Versatility: This welding technique can be used to join PVC materials of different shapes, sizes, and thicknesses. It offers flexibility in design and allows for the creation of complex assemblies.
- Consistency: Hot plate welding provides consistent and uniform heating, resulting in reliable and high-quality welds. The precise control of temperature and pressure during the process ensures consistent weld strength and integrity.
- Cost-Effective: Hot plate welding is a cost-effective method, as it does not require any additional consumables or adhesives. By utilizing heat and pressure, it creates strong bonds without the need for additional materials, reducing costs and simplifying the welding process.
- Aesthetically Pleasing Welds: Hot plate welding produces clean and visually appealing welds. The heat from the platen creates a smooth and uniform bond between the PVC parts, eliminating the need for additional finishing or post-welding processes. This not only saves time and costs but also enhances the overall quality and perceived value of the welded parts.
Recent Advancements in Hot Plate Welding Technology
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in hot plate welding technology, further enhancing its efficiency, reliability, and versatility. These advancements include:
- Temperature Regulation: The integration of temperature sensors and feedback control systems allows for more precise temperature regulation during the welding process. This ensures consistent and optimal welding conditions, improving the quality and reliability of the weld joints.
- Advanced Heating Elements: The use of advanced materials, such as ceramic composites, for the heating element has enhanced heat transfer efficiency and durability. These materials enable more efficient heating and contribute to the overall performance of the hot plate welding process.
- Automation and Robotics: The integration of automation and robotics into hot plate welding systems has revolutionized the industry. Automated systems enable high-speed and consistent weld production, increasing productivity and reducing human error. This integration ensures repeatability and consistency in the welding process, resulting in superior quality weld joints.
- Sustainability Considerations: Hot plate welding also contributes to sustainability efforts in the field of plastic fabrication. By creating strong and durable bonds between PVC parts, it reduces the need for additional fasteners or adhesives that can contribute to waste and environmental impact. The process also minimizes the risk of material failure or separation over time, extending the lifespan of the assembled products.
Conclusion
Hot plate welding is an efficient and reliable method for joining PVC materials. By following the proper process and guidelines, manufacturers can achieve strong and durable welds that meet their specific requirements. Whether it is for industrial applications or everyday use, hot plate welding offers a versatile and effective solution for joining PVC materials. With its ability to create strong bonds, work with various plastic materials, and produce aesthetically pleasing welds, hot plate welding continues to be a valuable technique in various industries. Continuous advancements in hot plate welding technology further enhance its performance and expand its applications in the ever-evolving field of plastic fabrication. Manufacturers can leverage these advancements to achieve superior quality, increased productivity, and cost-effectiveness in their production processes while also contributing to sustainable manufacturing practices.





