What is a Booster in Ultrasonic Welding?
Ultrasonic welding is a widely used technique for joining materials using high-frequency vibrations. It is a solid-state welding process that offers numerous advantages such as speed, efficiency, and reliability. One of the key components in ultrasonic welding is the booster, also known as an amplitude transformer. In this article, we will delve into the details of what a booster is, its role in the ultrasonic welding process, its characteristics, its importance in various industries, and the future advancements in booster technology.
Understanding Ultrasonic Welding
Before we dive into the specifics of a booster, let's briefly understand the basics of ultrasonic welding. Ultrasonic welding utilizes high-frequency mechanical vibrations to create a strong bond between materials. It is commonly employed in industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, packaging, and textiles, where precise and durable joining is essential.
The process of ultrasonic welding involves applying pressure and ultrasonic vibrations to the materials being joined. The vibrations, typically in the range of 20 to 40 kHz, generate heat at the interface of the materials, causing them to melt and form a bond. The result is a fast, efficient, and reliable welding method that does not require additional materials such as adhesives or solder.
The Role of a Booster in Ultrasonic Welding
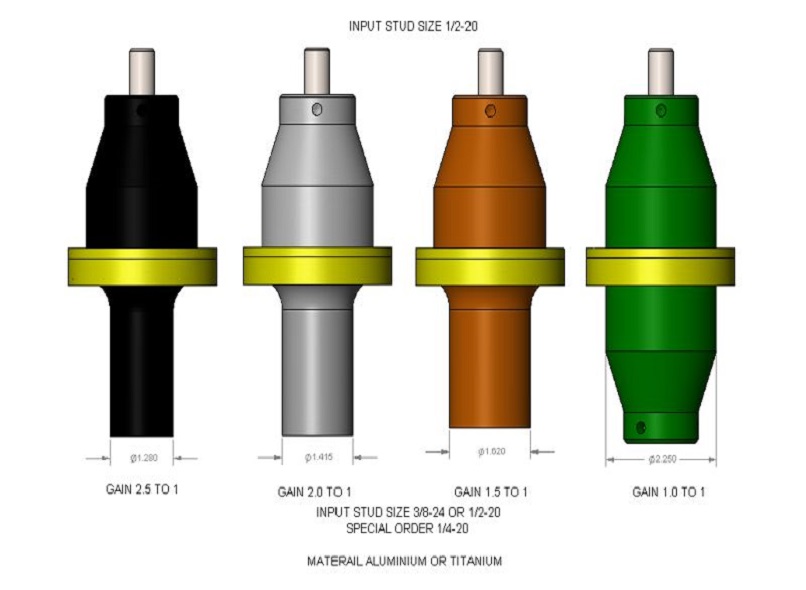
Now, let's focus on the booster and its significance in ultrasonic welding. A booster, as mentioned earlier, is an essential component that amplifies the amplitude of the ultrasonic vibrations generated by the transducer. The transducer, which converts electrical energy into mechanical vibrations, is the primary source of these vibrations.
However, the vibrations produced by the transducer may not have sufficient amplitude to create a strong weld. This is where the booster comes into play. The booster is designed to increase the amplitude of the vibrations before they are transmitted to the welding tool or horn. By increasing the amplitude, the booster enhances the welding efficiency and ensures a more effective transfer of energy to the materials being joined.
Characteristics of a Booster
Boosters used in ultrasonic welding are typically made of high-quality materials such as titanium or aluminum. These materials possess excellent mechanical properties and can withstand the high-frequency vibrations involved in the welding process. The boosters are carefully designed to match the resonance frequency of the transducer and optimize the amplitude amplification.
The shape and size of the booster can vary depending on the specific application and welding requirements. The design considerations include factors such as the type of materials being joined, the desired welding strength, and the geometry of the parts. Additionally, the booster is often equipped with acoustic impedance matching layers to improve energy transmission and minimize reflections.
Importance of Boosters in Various Industries
Boosters play a crucial role in ultrasonic welding across various industries. In the automotive industry, boosters are used for joining plastic components, such as interior trim, door panels, electrical connectors, and air ducts. They ensure secure and durable connections, contributing to the overall safety and reliability of the vehicles.
In the electronics industry, boosters are utilized for bonding wires, microchips, and other electronic components. The precise and reliable joining provided by ultrasonic welding with boosters ensures the integrity of the electronic devices, minimizing the risk of failure and improving performance.
In the medical device industry, boosters are essential for assembling components of medical devices, such as syringes, catheters, blood filters, and pacemakers. The ultrasonic welding process with boosters guarantees a hygienic and secure bond, critical for the safety and effectiveness of medical devices.
Furthermore, boosters are widely employed in the packaging industry for sealing various types of packaging materials, including blister packs, tubes, bottles, and food containers. The use of ultrasonic welding with boosters ensures leak-proof seals, extending the shelf life of the packaged products and enhancing customer satisfaction.
In the textile industry, boosters find application in joining fabrics, creating seamless garments, and assembling textile-based products. The precise control and energy efficiency of ultrasonic welding with boosters make it a preferred choice for textile manufacturers.
Future Advancements in Booster Technology
As technology continues to advance, so does the field of ultrasonic welding and booster technology. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on optimizing booster designs, exploring new materials with improved properties, and enhancing the overall performance of ultrasonic welding systems.
Future advancements in booster technology may include the development of smart boosters that can dynamically adjust their amplitude amplification based on the welding requirements. Additionally, advancements in materials science may lead to the discovery of new materials that offer even better performance characteristics, such as higher amplitude amplification and increased durability.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into ultrasonic welding systems may enable real-time monitoring and optimization of the ultrasonic welding process, including the performance of the booster. This can lead to improved process control, reduced defects, and enhanced productivity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a booster is a crucial component in ultrasonic welding that plays a significant role in enhancing the welding process. By amplifying the amplitude of the ultrasonic vibrations, the booster ensures a strong and reliable bond between materials. Understanding the importance of a booster in ultrasonic welding can help in achieving optimal results in various industries.
The effective utilization of boosters in ultrasonic welding can lead to improved productivity, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced weld quality. As technology advances, further research and development efforts in booster technology will continue to drive innovation and improvements in ultrasonic welding systems. With continuous advancements in ultrasonic welding and booster technology, this versatile joining technique will continue to find applications in various industries, contributing to efficient and high-quality manufacturing processes.





