Ultrasonic Welding Machine Components Explained

Ultrasonic welding is a highly effective and widely used method for joining thermoplastic materials, metals, and composite materials through the application of high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations.
Knowing the components of a welding machine is conducive to achieving the best results in the welding process. In this article, we explore the various parts and functions of a welding machine, and how they contribute to the overall efficiency and performance of ultrasonic welding systems.

Table of Contents
Key Components of Ultrasonic Welding Machines
Functionality and Benefits of Each Component
Individual Applications of Ultrasonic Components
Ultrasonic Welding Components Common Issues and Maintenance Tips
FAQs
Conclusion
Key Components of Ultrasonic Welding Machines
The main components of a welding machine are The Generator, Press, Transducer, Booster, Sonotrode, Fixture, Power Supply Units, and Control Systems.
Each of these components works in harmony to help ensure that ultrasonic vibrations are properly generated, transmitted, and applied to the materials being welded.
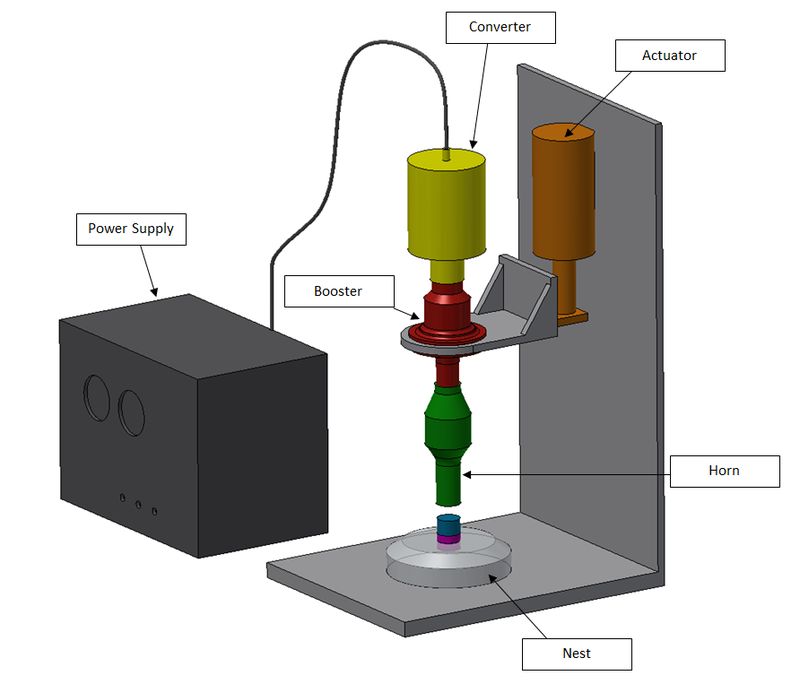
Functionality and Benefits of Each Component
Understanding the functionality and benefits of each component of a welding machine can help optimize the welding system for specific applications. Here is each part of a welding machine and its functions and benefits.
The Generator
Functionality:
The generator, as a component of a welding machine, is responsible for converting standard electrical power into a high-frequency electrical signal, typically ranging between 20 kHz and 70 kHz. This signal is then transmitted to the transducer, which converts it into mechanical ultrasonic vibrations.
Benefits:
- Precise Power Control: The generator offers precise control over the power output, allowing the operator to fine-tune the intensity of the ultrasonic waves.
- Energy Efficiency: It ensures that energy is efficiently transferred to the transducer, minimizing energy loss during the welding process.
- Consistency: A high-quality generator ensures that the machine operates consistently over extended periods, reducing the chances of welding defects.
The Press
Functionality:
The press ensures that pressure is applied uniformly across workpieces. It is one of the core parts of welding machines and its function is to exert the necessary force to fuse the materials together. Common applications include:
Benefits:
- Precise Pressure Application: It ensures that consistent pressure is applied, leading to uniform welds.
- Reduced Welding Time: By maintaining continuous pressure, the press accelerates the welding process, reducing cycle times.
- Versatility: The press can be customized for various materials and part shapes, enhancing the flexibility of the ultrasonic welding machine.
The Transducer
Functionality:
The transducer is a key part of the welder components, as it converts the high-frequency electrical signals from the generator into mechanical vibrations. This is achieved using piezoelectric crystals, which can expand and contract rapidly when subjected to an electrical field.
Benefits:
- High-Frequency Vibration Generation: The transducer produces ultrasonic vibrations with high precision, ensuring a clean and effective welding process.
- Durability: Modern transducers are designed for long-term use with minimal degradation in performance.
- Accuracy: The transducer ensures the accurate transmission of vibrations, critical for achieving the desired weld quality.
The Booster
Functionality:
The booster, also an essential part of a welding machine, amplifies the mechanical vibrations generated by the transducer. This amplification increases the amplitude of the ultrasonic waves, which is used for producing sufficient heat at the interface of the welded materials.
Benefits:
- Improved Energy Transfer:The booster helps in transmitting stronger ultrasonic energy to the welding area, resulting in a stronger and more reliable bond.
- Customization:By adjusting the booster, the amplitude of vibrations can be tailored for different materials and weld types.
- Consistency in Output: The booster ensures that the vibrations remain consistent, regardless of the duration of the welding cycle.
The Sonotrode
Functionality:
The sonotrode, also known as the horn, further amplifies and focuses the ultrasonic vibrations onto the materials being welded. It is custom designed to match the frequency of the vibrations and the specific geometry of the workpieces.
Benefits:
- Focused Energy Application: The sonotrode directs ultrasonic energy precisely onto the weld area, ensuring maximum heat generation at the interface.
- Weld Quality: It helps achieve strong, high-quality welds by applying the right amount of energy to the correct location.
- Material Compatibility: The design of the sonotrode can be optimized for different materials, making it a versatile component for various applications.

The Fixture
Functionality:
The fixture holds the workpieces in place during the welding process. It ensures that the materials are properly aligned and that the ultrasonic energy is applied precisely at the joint interface.
Benefits:
- Accurate Alignment: The fixture ensures that the parts are properly positioned, preventing misalignment during welding.
- Reduced Waste: Properly aligned workpieces reduce the likelihood of weld defects, minimizing material waste.
- Customizability: Fixtures can be designed to hold a variety of part shapes and sizes, enhancing the flexibility of the ultrasonic welding system.
Power Supply Units
Functionality:
The power supply unit provides the electrical power necessary to operate the ultrasonic welding machine. It converts the input power (typically AC) into a stable and high-frequency current for the generator.
Benefits:
- Reliable Power Delivery: Power supply units ensure that the ultrasonic welding system receives a steady and reliable supply of power, maintaining consistent performance.
- Efficiency: The power supply minimizes energy loss, ensuring that the ultrasonic machine operates at its peak efficiency.
- Safety: Modern power supply units are equipped with safety features to protect both the machine and the operator during the welding process.
Control Systems
Functionality:
Control systems manage all the operational parameters of the ultrasonic welding machine, including power, pressure, frequency, and time. These systems ensure that the machine operates within optimal parameters, adjusting as needed for different welding requirements.
Benefits:
- Automation: Control systems automate the entire welding process, ensuring consistency and reducing the need for manual adjustments.
- Precision: The system ensures that the welding parameters are tightly controlled, leading to consistent welding every time.
- Real-time Monitoring: Advanced control systems feature sensors that monitor the process in real-time and adjust settings to maintain optimal welding conditions.
Individual Applications of Ultrasonic Components
Each component of a welding machine is designed to meet specific requirements for different materials, part shapes, and welding conditions. Below, we'll explore the individual applications of each key welding machine component.
The Generator - Applications
The generator is essential in a variety of industries where high precision and energy control are needed. Common applications include:
- Automotive Industry: For joining plastic components like dashboards, interior trims, and wiring harnesses.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Used in the assembly of small electronic components such as connectors and sensors.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: For joining thermoplastic parts used in medical devices and disposable items like syringes and IV tubes.
The Press - Applications
The press ensures that pressure is applied uniformly across workpieces. Common applications include:
- Packaging Industry: Used to join plastic films and packaging materials for a secure seal.
- Textile Industry: For joining fabrics and textiles in a way that avoids stitching or gluing.
- Consumer Goods: In the production of durable plastic parts like phone cases, appliances, and household items.
The Transducer - Applications
The transducer plays a vital role in generating the ultrasonic vibrations needed for the welding process. It is applied in:
- Aerospace Manufacturing: For joining lightweight composite materials and components for aircraft.
- Electrical Components: In joining connectors and terminals in electronic devices.
- Medical Equipment: Used in the welding of medical components that require a precise and clean joining process.
The Booster - Applications
The booster amplifies the ultrasonic vibrations and is used in:
- Plastic Welding: Especially in high-precision plastic welding applications like automotive parts and medical devices.
- Metals Welding: For joining thin metal sheets and parts, especially in electronics and electrical industries.
- Packaging Industry: Used for the welding of multilayer packaging materials and sealing.
The Sonotrode - Applications
The sonotrode focuses on ultrasonic energy at the welding point. It is widely used in:
- Packaging and Sealing: For sealing plastic packaging and materials that require a precise, high-quality joint.
- Automotive Industry: To weld components like airbags, bumpers, and fuel tank assemblies.
- Medical Devices:For precise and clean welding of small medical parts such as syringes, tubes, and catheters.
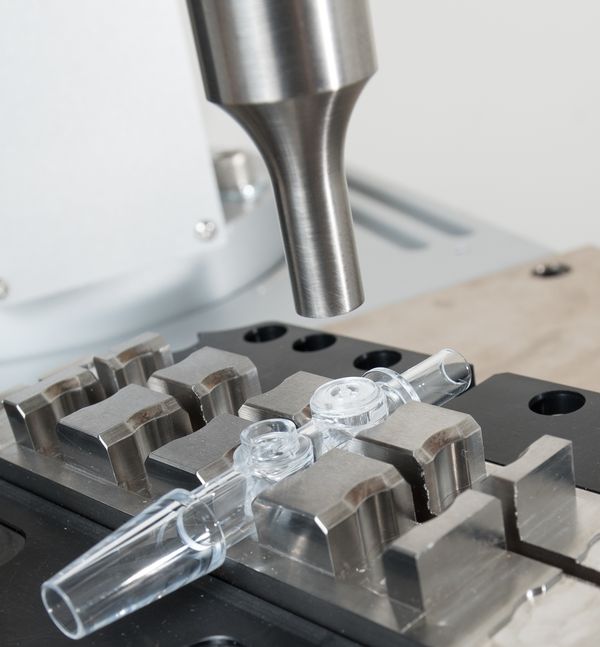

The Fixture - Applications
The fixture ensures proper alignment of parts during welding. It finds its applications in:
- Electronics: For aligning delicate components in high-precision welding.
- Medical Devices: Used in aligning small parts for accurate, high-quality joints.
- Plastic Components: To maintain the alignment and integrity of complex plastic assemblies.
Power Supply Units - Applications
The power supply unit provides the energy needed for ultrasonic welding. It is applied in:
- Manufacturing of Electronics: Ensures efficient power delivery to meet the high demands of electronics assembly.
- Plastic Part Welding: Powers the welding machine for consistent energy output, essential in mass production.
- Automotive Industry: Supplies reliable energy for the welding of automotive parts.
Control Systems - Applications
Control systems manage the ultrasonic welding process for different applications:
- Automotive Industry: For precise and repeatable welding of components like connectors, seals, and sensors.
- Consumer Electronics: In electronics manufacturing for high-quality, automated assembly.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: For strict quality control in the production of medical parts requiring sterile, precise welds.
Ultrasonic Welding Components Common Issues and Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance and quick identification of problems can significantly prolong the lifespan of welding machine components and maintain optimal welding performance.
Below are some common issues encountered in welding machines, along with maintenance tips for each component. <See plastic welding tips>
The Generator
Common Issues:
- Overheating: The generator may overheat due to improper cooling or a malfunctioning cooling system. Overheating can cause erratic power output or even damage the system.
- Power Fluctuations: The generator may experience voltage irregularities or power surges, leading to inconsistent welding quality.
Maintenance Tips:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean air filters and vents to ensure adequate cooling for the generator.
- Check Wiring Connections: Inspect wiring and connectors for wear and tear, as poor connections can lead to power issues.
- Test Voltage Regularly: Use a multimeter to ensure the generator is producing the correct voltage and frequency.

The Press
Common Issues:
- Pressure Loss: If the press system isn't maintaining consistent pressure, it can lead to poor weld quality, incomplete bonds, or part misalignment.
- Misalignment: The press may lose its alignment due to mechanical wear, leading to inconsistent pressure application.
Maintenance Tips:
- Check Hydraulic System: Regularly inspect the hydraulic system for leaks or worn-out seals.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Lubricate all moving components to ensure smooth operation.
- Alignment Calibration: Periodically check and calibrate the alignment of the press to ensure it applies even pressure.
The Transducer
Common Issues:
- Decreased Vibration Efficiency: Over time, the transducer may lose its efficiency in converting electrical signals into ultrasonic vibrations.
- Cracked Piezoelectric Crystals: The piezoelectric crystals inside the transducer can crack, leading to reduced performance.
Maintenance Tips:
- Regular Inspection: Regularly check the transducer for signs of physical damage or cracks in the piezoelectric material.
- Frequency Testing: Periodically test the frequency to ensure it is within the optimal range for efficient welding.
- Replace Worn-out Parts: If the transducer is no longer functioning at full capacity, it's essential to replace the crystals.
The Booster
Common Issues:
- Amplitude Loss: The booster may experience a loss of amplitude, leading to a decrease in ultrasonic energy at the welding interface.
- Cracks or Fatigue: The booster may crack due to repeated stress, which can result in energy loss.
Maintenance Tips:
- Regular Amplitude Testing:Check the amplitude of the booster regularly and replace it if it falls below optimal levels.
- Inspect for Cracks: Look for any signs of cracks or wear due to fatigue, especially around the high-stress points.
- Keep Clean: Clean the booster's surfaces regularly to prevent contamination that could interfere with energy transmission.
The Sonotrode (Horn)
Common Issues:
- Surface Damage: Prolonged use of the sonotrode can lead to surface wear, which can affect the efficiency of the ultrasonic energy transfer.
- Frequency Misalignment: If the sonotrode's frequency doesn't match the system's generator frequency, it can lead to ineffective welding.
Maintenance Tips:
- Regular Surface Checks: Inspect the surface of the sonotrode for signs of wear, nicks, or cracks, and replace it when necessary.
- Frequency Testing: Ensure that the sonotrode's frequency is in sync with the generator's output for optimal energy transfer.
- Polish and Clean: Clean and polish the sonotrode regularly to avoid contaminants or buildup that could impair performance.
The Fixture
Common Issues:
- Improper Alignment: If the fixture isn't properly aligned, the workpieces won't be held securely during welding, leading to poor weld quality.
- Wear and Tear: Fixtures may wear out over time, particularly if used with a variety of materials or under heavy-duty conditions.
Maintenance Tips:
- Check Alignment Regularly: Ensure that the fixture aligns properly with the workpieces during each welding cycle.
- Inspect for Wear: Look for any wear and tear, especially on the clamps and holding areas, and replace worn parts.
- Ensure Cleanliness: Keep the fixture clean from dust, debris, and contaminants that can interfere with alignment and pressure application.
Power Supply Units
Common Issues:
- Inconsistent Power Output: Power supply issues, such as sudden voltage dips or spikes, can lead to welding defects.
- Component Failures: Over time, the components in the power supply unit can degrade, affecting the overall functionality of the ultrasonic welding machine.
Maintenance Tips:
- Voltage Monitoring: Regularly monitor the voltage output to ensure stability and detect any issues early.
- Replace Worn Components:Replace any worn or faulty components in the power supply unit as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
- Keep Clean: Ensure the power supply unit is clean and free of dust to avoid overheating.
Control Systems
Common Issues:
- Faulty Sensors: If sensors in the control system fail, they may not adjust the parameters properly, leading to poor weld quality.
- Software Malfunctions: Control system software can sometimes malfunction or become outdated, leading to errors in the welding process.
Maintenance Tips:
- Sensor Calibration: Regularly calibrate sensors to ensure accurate readings and adjustments.
- Software Updates: Keep the control system software up to date to prevent malfunctions and optimize performance.
- Periodic Testing: Perform regular tests to ensure the system's response to changes in power, pressure, and other parameters is accurate.
FAQs
What material is used for ultrasonic horns?
Ultrasonic horns (sonotrodes) are typically made from titanium or aluminum. Titanium is favored for its strength, lightweight nature, and excellent resistance to wear, while aluminum is used for its cost-effectiveness and lightweight properties in less demanding applications.
What is the ratio of ultrasonic boosters for welding?
The ultrasonic booster typically has a 2:1 or 3:1 ratio, meaning it can amplify the amplitude of the ultrasonic vibrations by two or three times. This amplification is necessary for increasing the energy focused on the weld area, improving the welding efficiency.
How does the frequency of the generator affect the welding quality?
The frequency of the generator determines the rate at which ultrasonic waves are emitted. A higher frequency typically results in finer, more precise welds, while a lower frequency is used for welding thicker materials. The right frequency ensures strong, clean, and reliable welds.
How does the booster contribute to the overall efficiency of the ultrasonic welding process?
The booster amplifies the amplitude of ultrasonic vibrations, ensuring that enough energy is concentrated at the weld interface. This increased energy improves the effectiveness of the welding process, allowing for faster weld times and better joint strength.
What are the key differences between the components of an ultrasonic welding machine and those of other welding machines?
Unlike traditional welding machines, ultrasonic welding machines rely on high-frequency sound waves rather than heat to fuse materials. Components like the transducer, booster, and sonotrode are specific to ultrasonic welding and allow for precise control over the energy applied, making it ideal for welding delicate or small components.
What is the basic parts of an arc welding machine?
The basic parts of an arc welding machine include the power source (which provides electrical energy), the electrode holder (which holds the welding electrode), the work clamp (to complete the electrical circuit), and the electrode, which melts to form the weld bead.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic welding machines are vital tools for creating strong, reliable joints in a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and composites. By understanding the key components, their functionality, and common maintenance tips, manufacturers can ensure their ultrasonic welding machines perform optimally.
Regular maintenance and quick resolution of issues can significantly extend the lifespan of the ultrasonic welding machine and improve welding quality, making it indispensable in industries such as automotive, medical device manufacturing, and electronics assembly.






