Unlocking the Potential: Exploring the Process of Hot Plate Welding Polypropylene
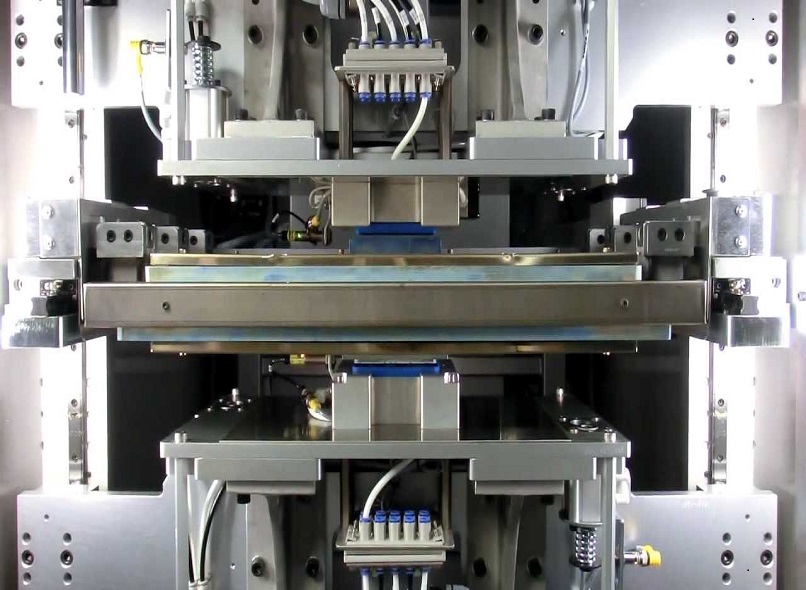
Hot plate welding has emerged as a widely adopted and efficient technique for joining thermoplastic components, with polypropylene being one of the commonly welded materials. This process involves the strategic use of a heated metal plate to melt the surfaces of the polypropylene pieces, followed by the application of pressure to create a strong and durable bond. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the step-by-step process of hot plate welding polypropylene, highlighting its advantages, considerations, and recent advancements.
Step-by-Step Guide to Hot Plate Welding Polypropylene
- Material Preparation: Start by gathering the polypropylene pieces that require welding. Ensure that they are clean and free from any contaminants that could hinder the welding process. Pay particular attention to the surface finish, as a smooth surface promotes optimal adhesion.
- Equipment Setup: Position the hot plate welding machine on a stable surface, ensuring it is in proper working condition. Consult the manufacturer's guidelines to determine the appropriate temperature for welding polypropylene. Adjust the temperature of the hot plate accordingly, considering the specific requirements of polypropylene.
- Clamping: Carefully place the polypropylene pieces onto the hot plate, ensuring proper alignment. Secure the pieces in place using clamps or fixtures to maintain alignment during the welding process. This step is crucial for achieving a tight and uniform joint.
- Heating the Surfaces: Activate the hot plate and allow it to reach the designated temperature. The heat generated by the hot plate will soften and melt the surfaces of the polypropylene pieces, preparing them for bonding. It is essential to closely monitor the temperature to prevent overheating or damaging the polypropylene.
- Joining the Materials: Once the surfaces are adequately heated, remove the polypropylene pieces from the hot plate and quickly bring them together. Apply sufficient pressure to ensure proper contact between the melted surfaces. The pressure helps facilitate material flow and promotes a strong bond. The specific pressure and duration of pressure application depend on the polypropylene material and the desired strength of the weld joint.
- Cooling and Solidification: Hold the joined pieces together for a predetermined amount of time to allow the melted plastic to cool and solidify. This cooling process is crucial for ensuring the long-term strength and stability of the weld joint. The cooling time required may vary based on factors such as the size and thickness of the welded components.
- Finishing Touches: Once the weld joint has cooled and solidified, inspect it for any defects or imperfections. Carefully remove any excess material or flash using appropriate tools to achieve the desired final shape and appearance. Conduct a thorough examination to ensure the weld is of high quality and meets the required specifications.
Advantages and Considerations for Hot Plate Welding Polypropylene
Hot plate welding offers several advantages when used for polypropylene:
- High Strength: Hot plate welding creates weld joints that exhibit high strength and durability, comparable to the original polypropylene material. This ensures the longevity and reliability of the assembled products.
- Leak-Tight Seals: The hot plate welding process produces weld joints with excellent sealing properties. This makes it ideal for applications that require leak-tight connections, such as in the automotive, medical, and plumbing industries.
- Versatility: Hot plate welding can be performed on polypropylene components of various sizes and complexities. It is particularly effective for joining large or irregularly shaped parts that may be challenging to weld using other techniques.
- Compatibility: Polypropylene is highly compatible with hot plate welding. The process effectively fuses polypropylene pieces together, creating strong and uniform welds.
While hot plate welding is a versatile and efficient method for joining polypropylene, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
- Temperature Sensitivity: Polypropylene is sensitive to temperature, and excessive heat can lead to degradation or undesirable changes in its properties. Careful temperature control is crucial to prevent any adverse effects during the welding process.
- Material Compatibility: Although hot plate welding is well-suited for welding polypropylene, it may not be compatible with all thermoplastic materials. It is essential to assess the compatibility of different materials before attempting the hot plate welding process.
- Process Control: Achieving optimal weld quality requires precise control of the heating and cooling cycles. Overheating or insufficient fusion can result in weak welds. Manufacturers must carefully consider the material properties and design requirements to ensure proper process control.
Recent Advancements in Hot Plate Welding Technology
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in hot plate welding technology, further enhancing its efficiency, reliability, and versatility. These advancements include:
- Temperature Regulation: The integration of temperature sensors and feedback control systems allows for more precise temperature regulation during the welding process. This ensures consistent and optimal welding conditions, improving the quality and reliability of the weld joints.
- Advanced Heating Elements: The use of advanced materials, such as ceramic composites, for the heating element has enhanced heat transfer efficiency and durability. These materials enable more efficient heating and contribute to the overall performance of the hot plate welding process.
- Automation and Robotics: The integration of automation and robotics into hot plate welding systems has revolutionized the industry. Automated systems enable high-speed and consistent weld production, increasing productivity and reducing human error. This integration ensures repeatability and consistency in the welding process, resulting in superior quality weld joints.
- Sustainability Considerations: Hot plate welding also contributes to sustainability efforts in the field of plastic fabrication. By creating strong and durable bonds between polypropylene parts, it reduces the need for additional fasteners or adhesives that can contribute to waste and environmental impact. The process also minimizes the risk of material failure or separation over time, extending the lifespan of the assembled products.
In conclusion, hot plate welding is an effective and reliable method for joining polypropylene components. By following the step-by-step process and considering the advantages, considerations, and recent advancements, manufacturers can achieve strong and durable weld joints. Hot plate welding offers versatility, high strength, and leak-tight seals, making it a valuable technique in a wide range of industries. As technology continues to advance, the field of hot plate welding is poised to deliver even more efficient and sustainable joining solutions for polypropylene and other thermoplastic materials.





